Welcome, language enthusiasts, to another exciting discussion on languages! Today, we delve into the intriguing topic of Mandarin vs Chinese. Often used interchangeably, Mandarin and Chinese can create confusion among language learners. In this article, we aim to shed light on the distinctions between these terms and help you navigate the linguistic landscape of Taiwan and China with ease.

Understanding Mandarin
Mandarin is a specific dialect* of the Chinese language and is the most widely spoken dialect in China. With over a billion speakers, it is the official language of Taiwan and China. Mandarin is based on the Beijing dialect and is the standard form of Chinese used in education, media, and official communications. When people refer to learning “Chinese,” they often mean learning Mandarin. Mandarin is referred to as “普通話” (ㄆㄨˇ ㄊㄨㄥ ㄏㄨㄚˋ – pǔtōnghuà), meaning “common speech,” in China, and “國語” (ㄍㄨㄛˊ ㄩˇ – guóyǔ), meaning “national language,” in Taiwan.
Chinese as a Broad Term
Chinese, on the other hand, is a more comprehensive term that encompasses various languages and dialects spoken in different regions of China and Taiwan. These dialects include Mandarin, Cantonese, Shanghainese, Hokkien, Hakka, and many others. Each of these dialects has its own unique characteristics, pronunciation, and vocabulary. It’s important to note that these dialects can be mutually unintelligible, meaning speakers of one dialect may not understand another.
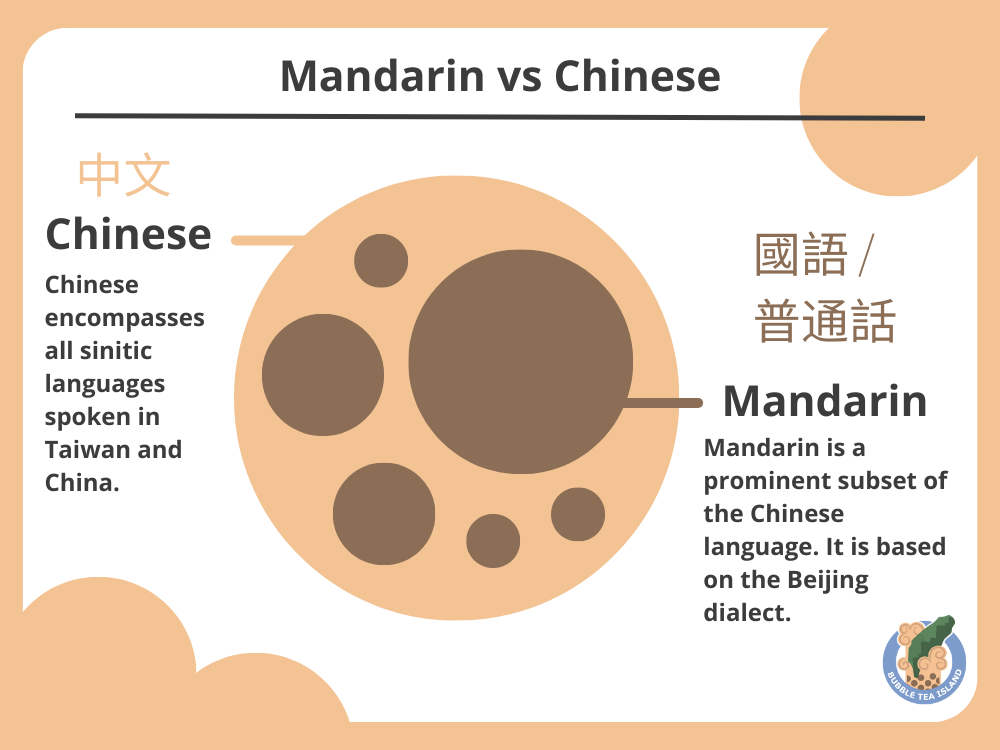
Mandarin as a Subset of Chinese
Mandarin is a prominent subset of the Chinese language. While Chinese is a broader term, Mandarin specifically refers to the standardized form of Chinese used across China and Taiwan. It serves as a lingua franca among speakers of different dialects and enables effective communication throughout the country. When Chinese people from different regions come together, they often communicate in Mandarin to ensure mutual understanding.
Written Chinese: A Unifying Script
While Mandarin is the spoken language, written Chinese acts as a unifying script across various dialects. The Chinese writing system, known as Hanzi, employs characters that represent words or concepts rather than sounds. This system allows speakers of different dialects to communicate in writing, as the characters have consistent meanings across regions. Although pronunciation varies across dialects, the written form remains largely consistent, allowing Chinese speakers from different regions to read and understand written texts.
Popularity and Influence
Mandarin’s dominance in China and Taiwan stems from its status as the official language and its widespread use in education, media, and business. Learning Mandarin offers numerous advantages, as it allows you to communicate with the majority of Chinese speakers. Additionally, with China’s growing global influence, Mandarin is becoming increasingly valuable in international contexts. It opens doors to career opportunities, cultural exchanges, and deeper connections with Chinese communities around the world.
In conclusion, the terms Mandarin and Chinese may appear interchangeable at first, but they carry distinct meanings. Mandarin refers specifically to the standardized dialect used in China and Taiwan, while Chinese encompasses a broader range of dialects spoken across different regions. Understanding the differences between Mandarin and Chinese is essential for anyone interested in exploring the rich linguistic and cultural tapestry of China and Taiwan. Embracing Mandarin opens doors to effective communication and opportunities in a country with a rich history and a promising future. So, whether you embark on learning Mandarin or delve into other fascinating Chinese dialects, you’re sure to embark on a rewarding linguistic journey.
*Note : The term “dialect” is officially used by both Taiwan and China; however, most linguists argue that “language” is a more appropriate term.

Join our Substack “Mandarin Zest“, where we regularly share intermediate to advanced Chinese learning content. Make sure to subscribe!

